Customer expresses intent; Communicate between the two parties; Provide analysis reports to customers; Reach a cooperation intention.
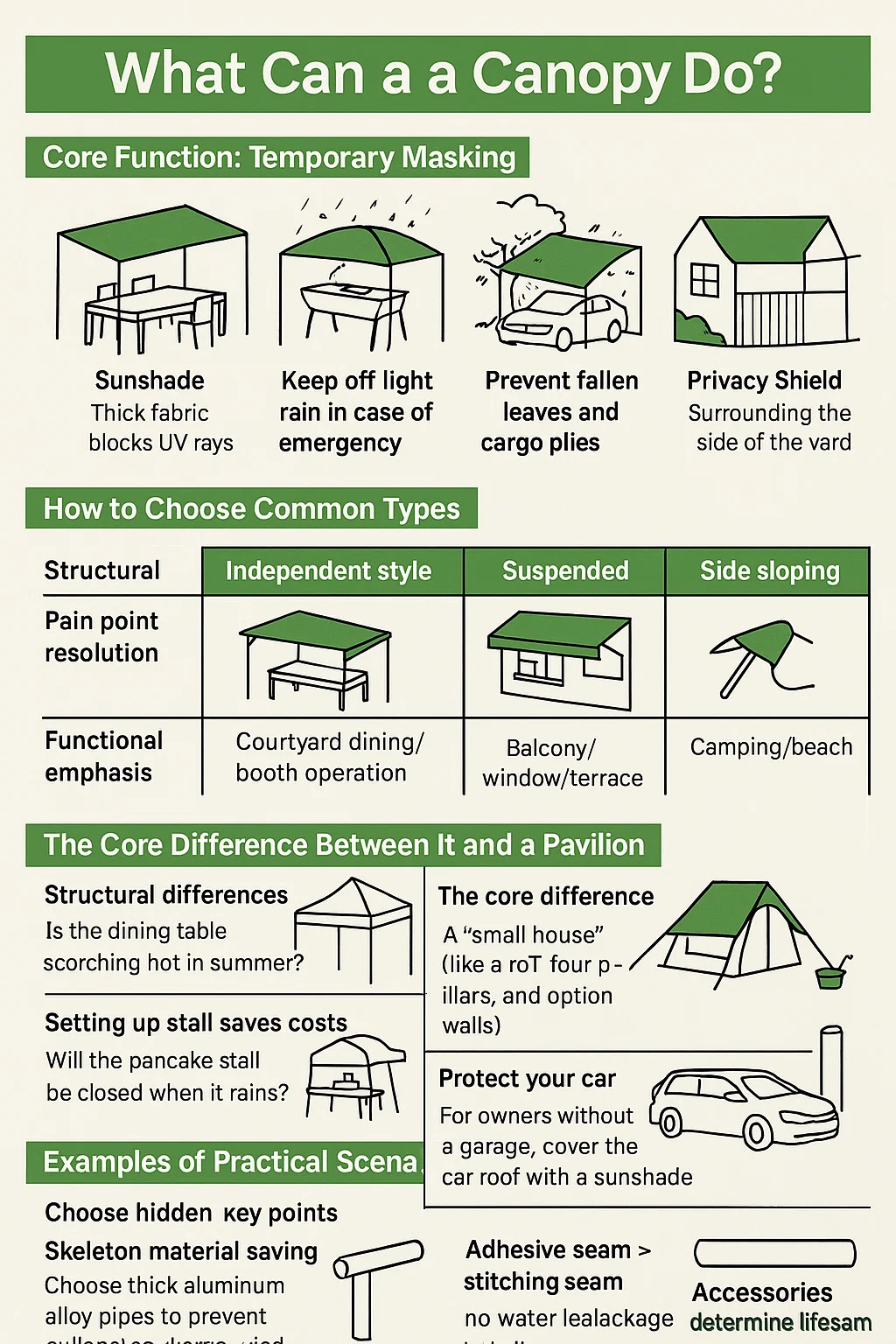
Canopies are "movable outdoor sunshades and rain barriers" - unlike fixed pavilions that require a foundation, they are supported by shelves or hung directly on objects, and can be collected after use. The essence is to quickly create a shadow for you, focusing on these characteristics:
1. Core function: Temporary masking
Sunshade → Thick fabric blocks UV rays, can't you move the shade under the tree? It will directly make a piece for you.
Keep off light rain in case of emergency → waterproof coating fabric can withstand light rain for a short time (don't expect a rainstorm), and it doesn't panic when it rains suddenly for outdoor barbecue.
Prevent falling leaves and bird droppings - Cover vehicles and cargo piles to save time for daily cleaning.
Privacy Shield → Surrounding the side of the yard to block the view of neighbors.
2. How to choose common types
| Type | Best For | Where It Shines | Watch Outs |
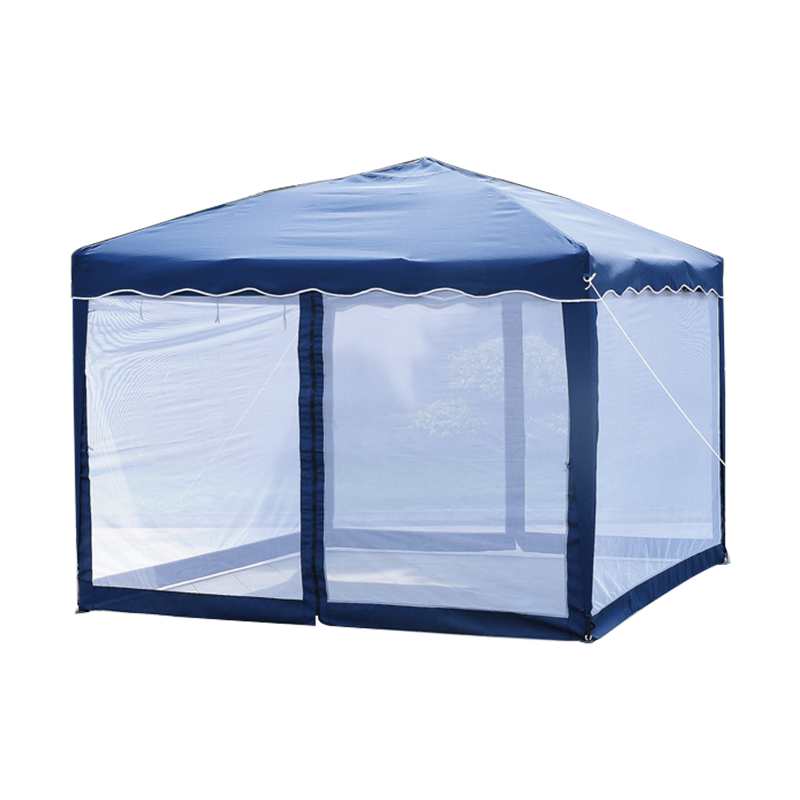
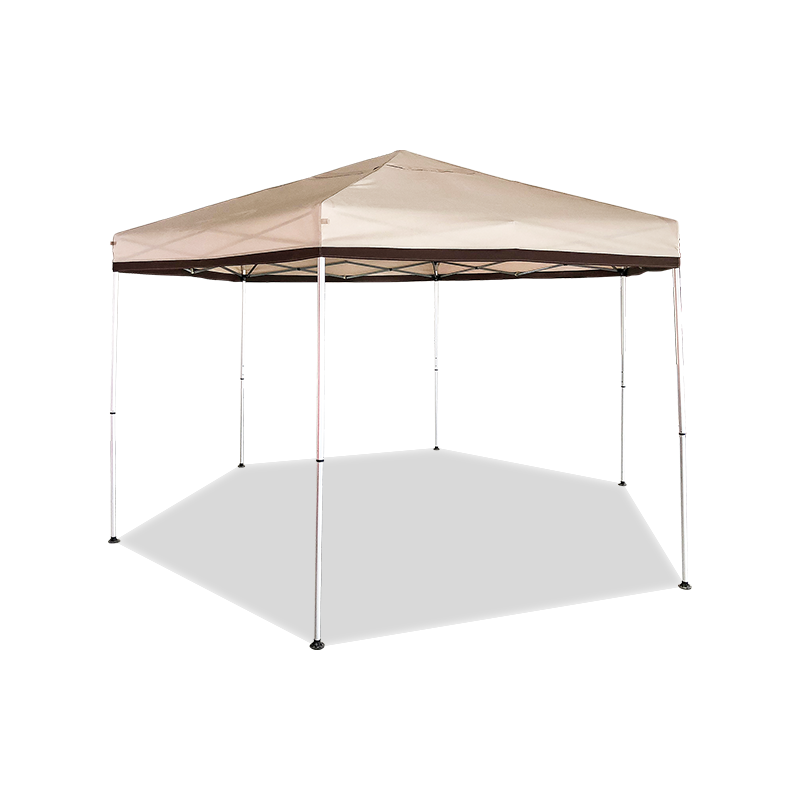
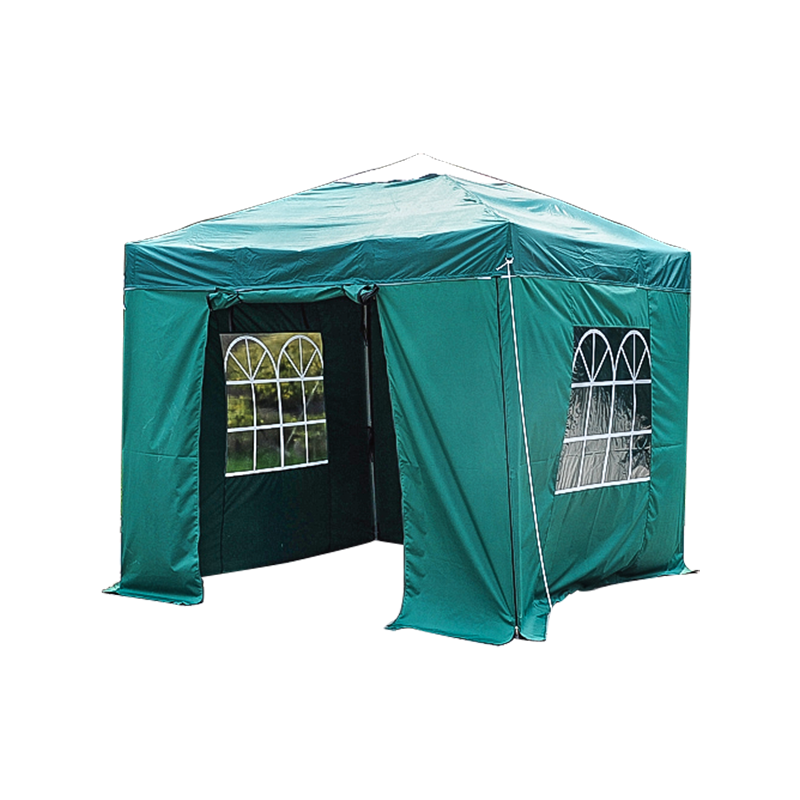
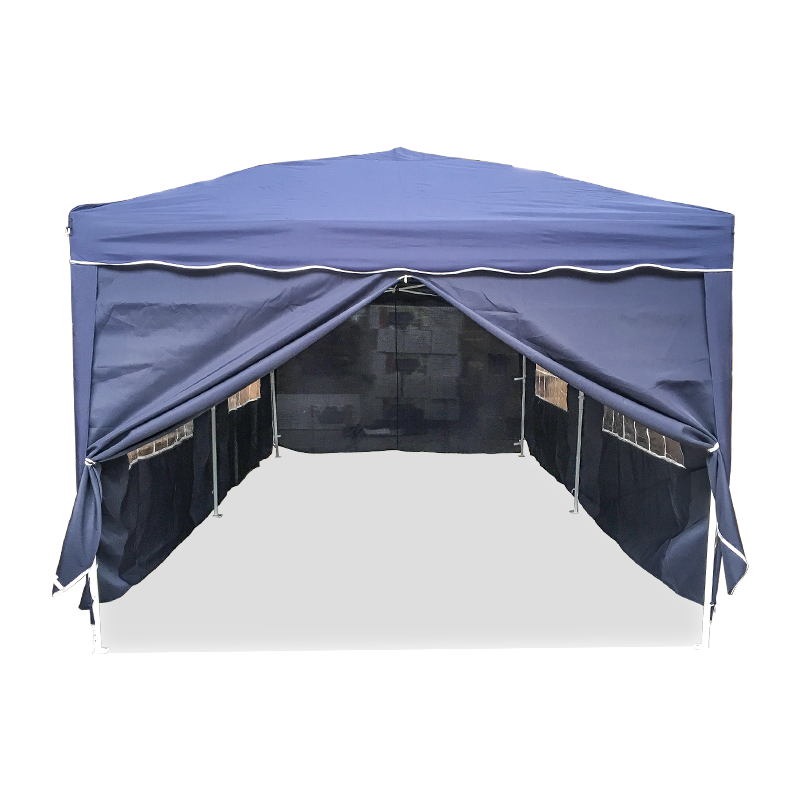
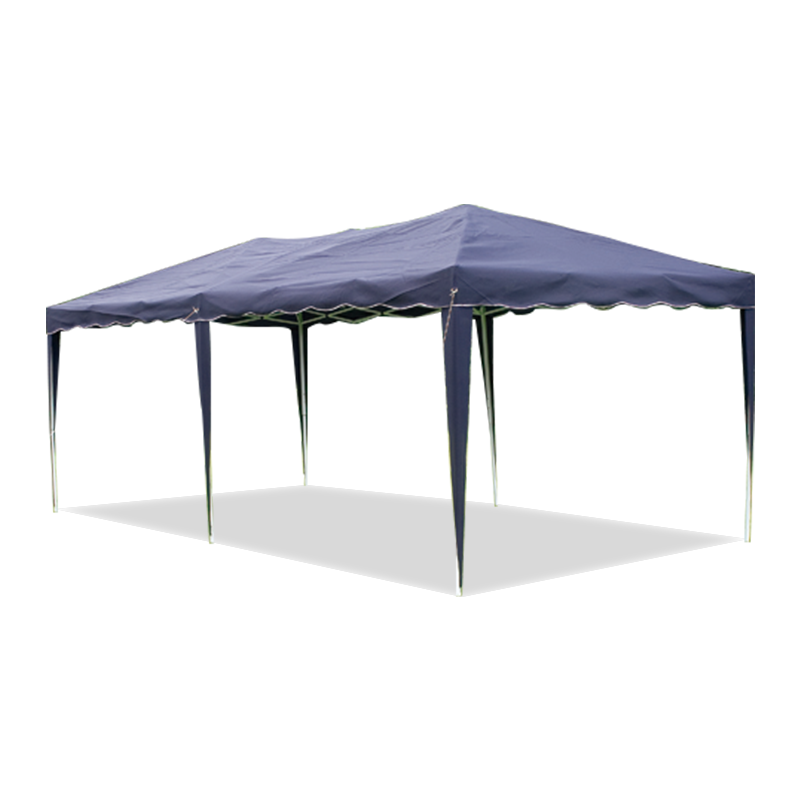
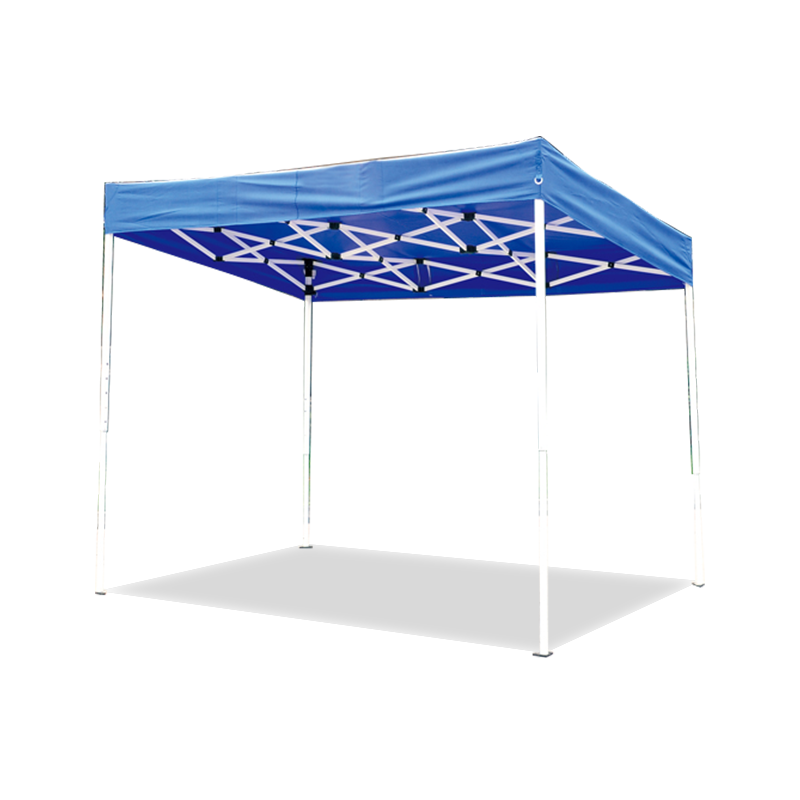
| Freestanding | • Backyard BBQs • Market stalls • Pop-up events | Sets up anywhere - no walls/trees needed. Lets you walk freely under all sides. | Needs heavy weights/stakes in wind. Avoid thin legs. |
| Wall-Attached (Awning style) | • House patios • Storefronts • Apartment balconies | Bolts to existing walls. Saves space, covers entryways perfectly. Lets rain runoff clear. | Requires drilling. Won’t cover standalone areas. |
| Offset/Pergola | • Driveways • Pool decks • Restaurant terraces | Covers wide areas with minimal posts (no center poles). Modern, open look. | Complex install. Needs pro measurement for slopes. |
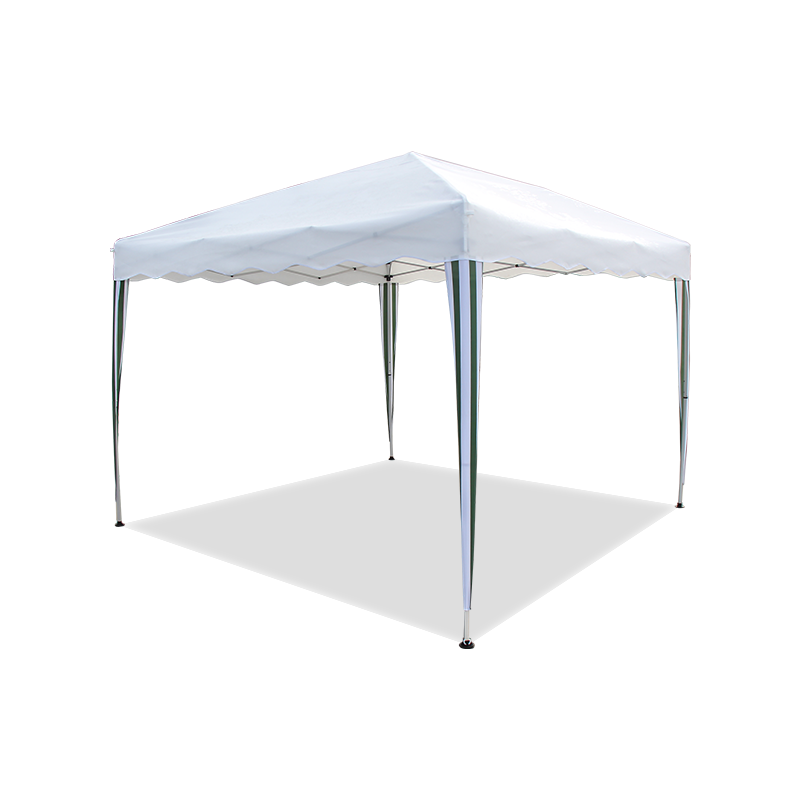
| Popup/Packable | • Beach days • Tailgates • Camping kitchens | Fits in a backpack. Goes up in <60 secs. Wet sandy? Hose it down. | Flimsy in storms. Short lifespan if used weekly. |
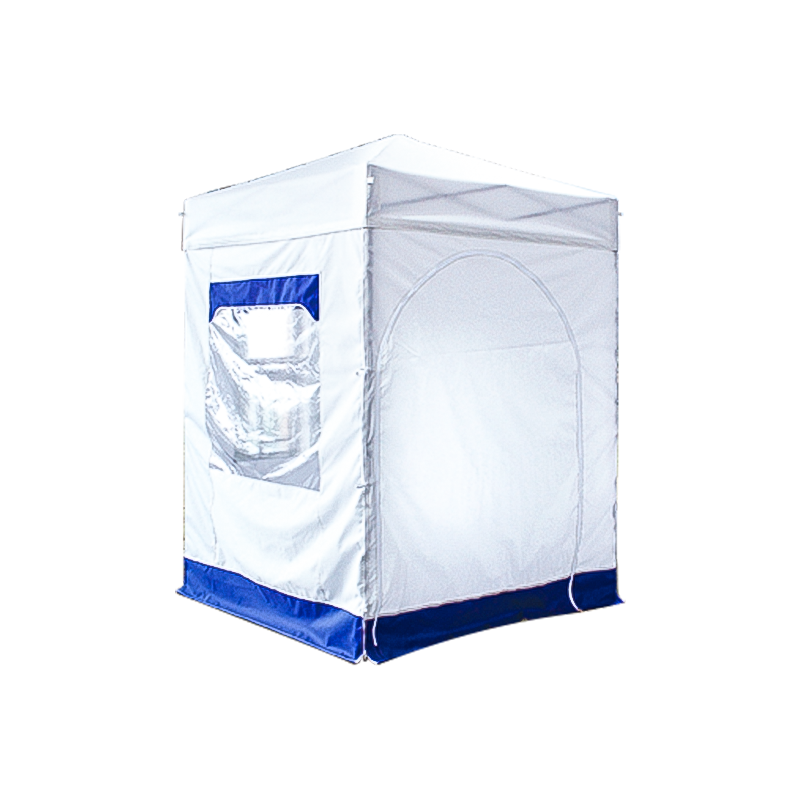
| Vehicle/Cargo | • Truck bed camping • RV shade • Equipment protection | Clamps to roof racks/trailers. Covers gear or creates instant garage. | Must match vehicle dimensions exactly. Check clamp compatibility. |
3. The core difference between it and a pavilion
Structural differences → The pavilion is a "small house" (with a roof, four pillars, and optional walls); The sunshade is a "single roof" (which may require hanging against a wall or on one side).
Portability → The sunshade is lighter (like a fishing umbrella when folded up), but the standalone roof has weaker wind resistance.
Functional emphasis → The pavilion emphasizes spatial protection; The sunshade focuses on covering the top of the head.
4. Examples of Practical Scenarios
Backyard emergency: Is the dining table scorching hot in summer? It only takes 10 minutes to set up the sunshade and start eating.
Setting up a stall to save costs: Will the pancake stall be closed when it rains? Pull out the tent and continue selling.
Protect your car: For owners without a garage, cover the car roof with a sunshade to prevent exposure to sunlight and aging.
Camping Extension Area: Install a sunshade outside the tent and store cooking utensils or wet shoes.
5. Choose hidden key points
Skeleton material saving → Choose thick aluminum alloy pipes to prevent collapse in strong winds. Iron pipes rust and thin aluminum pipes bend easily when exposed to wind.
Fabric seam inspection → adhesive seam>stitching seam, no water leakage in light rain. Touching the inner layer of the fabric with a coating feeling is considered qualified.
Accessories determine lifespan → Ground nails should have coarse threads that can withstand even sandy terrain; Choose a wide woven strap for the straps, and the nylon rope is easy to cut by hand.

 English
English Español
Español












